Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-13 Origin: Site









Polyethylene and polypropylene bags differ in several key ways that impact their performance and suitability for different tasks. A pe bag delivers flexibility and tear resistance, making it ideal for grocery and industrial packaging. Polypropylene bags, on the other hand, provide higher tensile strength, clarity, and chemical resistance, which suits food, retail, and medical uses. Polyethylene stands out for its softness and cost-effectiveness, while polypropylene excels in product visibility and durability. Choosing the right bags depends on the required balance of flexibility, strength, and heat tolerance.

Polyethylene bags are soft, flexible, and cost-effective, making them ideal for grocery, industrial, and cold storage uses.
Polypropylene bags offer higher strength, clarity, and heat resistance, perfect for food packaging, retail displays, and medical supplies.
Choose polyethylene bags for flexibility and moisture protection; pick polypropylene bags for durability, chemical resistance, and product visibility.
Both bag types are lightweight and recyclable, but local recycling options and proper disposal affect their environmental impact.
Matching the bag type to your product’s needs ensures better performance, cost savings, and sustainability.

Polyethylene and polypropylene bags differ at the molecular level, which shapes their performance in packaging. Polyethylene bags use repeated ethylene units, while polypropylene bags use repeated propylene units. This difference in chemical structure leads to unique characteristics for each material.
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Repeated ethylene units (-CH2-CH2-) | Repeated propylene units (-CH2-CH(CH3)-) |
| Density | 0.91 - 0.94 g/cm³ | 0.90 - 0.91 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 115 - 135°C | 130 - 171°C |
| Flexibility | More flexible | More rigid and stiff |
| Tensile Strength | LDPE: 1050-2100 psi; HDPE: 4550-6100 psi | 4000-5800 psi |
| Impact Resistance | Better impact resistance | Slightly less impact resistance |
| UV Stability | Less stable under UV exposure | Better UV stability |
| Barrier Properties | Better against moisture, water vapor, oxygen | Better against grease, oil, and chemicals |
| Moisture Absorption | 0.01% to 0.5% | 0.01% to 0.8% |
Polyethylene bags, including LDPE and HDPE, offer more flexibility and better impact resistance. Polypropylene bags provide higher rigidity and improved UV stability. These differences make each bag type suitable for specific packaging needs.
Physical properties set a pe bag apart from a polypropylene bag. Polyethylene bags show high flexibility and excellent elongation at break, making them ideal for applications that require stretch and softness. Polypropylene bags, in contrast, deliver greater stiffness and clarity, which benefits product visibility and structure.
| Bag Type | Strength & Durability | Volume (Size) | Weight | Environmental Impact & Recycling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE (Polyethylene) | Baseline standard; lighter | Moderate (6th rank) | Lightest; easy transport | High GHG emissions; non-biodegradable; contains harmful chemicals; recyclable but tedious |
| LDPE (Polyethylene) | Less strong than PP | Smaller volume | Light weight; easy transport | Similar environmental concerns as HDPE; non-biodegradable; recycling tedious |
| Non-woven PP | Stronger and more durable | Larger volume (2nd rank) | Heavier; harder to transport | High GHG emissions; non-biodegradable; recycling tedious |
| Woven PP | Stronger and more durable | Largest volume (1st rank) | Heavier; harder to transport | High GHG emissions; non-biodegradable; recycling tedious |
A pe bag, especially in LDPE form, can stretch up to 700% before breaking, while polypropylene bags maintain their shape and resist deformation. Polyethylene bags weigh less, which makes them easier to transport. Polypropylene bags, especially woven and non-woven types, offer superior strength and durability, supporting heavier loads and larger volumes.
Note: Both polyethylene and polypropylene bags resist many chemicals, but polypropylene bags excel in resistance to grease, oil, and solvents. Polyethylene bags perform better as barriers against moisture and oxygen.
Polyethylene and polypropylene bags serve different roles across industries due to their unique properties.
Polyethylene bags appear in grocery stores as shopping bags, in food packaging as freezer bags, and in industrial settings for shipping and storage. Their flexibility and low weight make them a top choice for everyday packaging.
Polypropylene bags find use in food packaging that requires heat resistance, such as microwaveable containers. They also appear in apparel packaging, medical supplies, and industrial sacks for products like fertilizer and chemicals.
Case studies highlight these trends:
Retailers and delivery services use reusable polyethylene and polypropylene bags to support sustainability and circular economy goals.
The apparel industry has reduced reliance on polyethylene bags by adopting recyclable and plastic-free alternatives.
Polypropylene bags play a key role in recycling and waste management, with organizations developing advanced recovery systems for these materials.
In the food and beverage sector, polypropylene bags provide packaging for coffee pods and other products that require high resistance to heat and chemicals.
Polyethylene bags dominate in applications where flexibility, light weight, and moisture protection are priorities. Polypropylene bags excel in situations that demand rigidity, clarity, and chemical resistance.
Polyethylene stands as the most widely produced synthetic polymer, with annual production exceeding 100 million tons. Manufacturers create several types of polyethylene, each with unique properties and applications. The three main types include:
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE): This type features a branched structure, giving it a density between 0.905 and 0.935 kg/m³. LDPE is soft and flexible, making it ideal for lightweight polyethylene bags and films.
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE): Produced as a copolymer, LLDPE offers higher impact and tensile strength than LDPE. It is commonly used for stretch films and heavy-duty bags.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE): With a density of 0.940 to 0.965 kg/m³, high-density polyethylene has a linear structure and high crystallinity. This results in rigid, durable polyethylene bags suitable for carrying heavier loads.
Note: Each type of polyethylene exists in multiple grades, allowing manufacturers to tailor polyethylene bags for specific uses, from short-term packaging to long-lasting industrial applications.
Polyethylene bags deliver a combination of flexibility, strength, and chemical resistance. The table below highlights key properties:
| Property | Polyethylene Bags |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | High, especially in LDPE and LLDPE |
| Impact Strength | Superior, retains flexibility at low temps |
| Low-Temperature Behavior | Excellent crack resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists moisture, acids, and alkalis |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower raw material and processing costs |
| Recyclability | Recyclable with proper management |
Polyethylene bags maintain performance in cold environments and resist brittleness, making them reliable for storage and transport.
Polyethylene bags offer several advantages:
Flexibility and softness allow easy handling and packing.
Superior impact strength prevents tearing and damage.
Reliable performance at low temperatures supports use in cold storage.
Lower production and processing costs make polyethylene bags affordable.
High recyclability supports sustainability goals.
These benefits explain why polyethylene bags remain a top choice for packaging and transport.
Polyethylene bags serve a wide range of industries and applications:
Food packaging, including bread, produce, and frozen items
Retail shopping bags and checkout sacks
Shipping and packaging for industrial goods
Agricultural films and protective covers
Waste management, such as garbage and trash bags
Polyethylene bags dominate the market due to their strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. High-density polyethylene bags, in particular, handle bulk packaging needs in agriculture, construction, and retail.
Polypropylene bags stand out in the packaging industry for their unique combination of rigidity, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. These bags maintain their shape under stress, offering moderate rigidity with high flexibility. Polypropylene bags can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for microwaveable food packaging and sterilization processes. Their chemical resistance protects contents from acids, alcohols, bases, and mineral oils, which is essential for industrial and food packaging applications. Polypropylene bags also feature low moisture absorption, which helps preserve product quality and extends shelf life.
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Rigidity/Flexibility | Moderate rigidity with high flexibility |
| Heat Resistance | High heat resistance, maintains toughness at elevated temperatures |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to many solvents, acids, and bases |
| Clarity | High clarity and gloss |
Polypropylene bags benefit from high fatigue resistance, allowing repeated use without significant wear.
Polypropylene bags offer several competitive advantages over other packaging solutions. Their high tensile strength and durability make them ideal for heavy-duty uses in agriculture, construction, and retail. These bags are lightweight and cost-effective, which reduces shipping costs and increases efficiency. Polypropylene bags resist moisture and pests, supporting long-term storage for food products. Laminated polypropylene bags provide extra protection against environmental factors and enhance branding with high-quality printing. The global market for polypropylene bags continues to grow, driven by demand in food, agriculture, and industrial sectors.
Sustainability initiatives, such as biodegradable and recycled polypropylene bags, are gaining traction as environmental regulations and consumer preferences evolve.
Polypropylene bags play a vital role in many industries due to their versatility and performance. In food packaging, these bags keep snacks, pet food, and agricultural products fresh and safe. Bulk polypropylene bags, such as FIBC, transport grains and powders securely, preventing contamination. The apparel industry uses polypropylene bags for backpacks, thermal wear, and socks because of their moisture-wicking properties. Industrial applications include sandbags for flood control and UN-certified bulk bags for material handling. Polypropylene bags dominate sectors that require durability, chemical resistance, and heat tolerance.
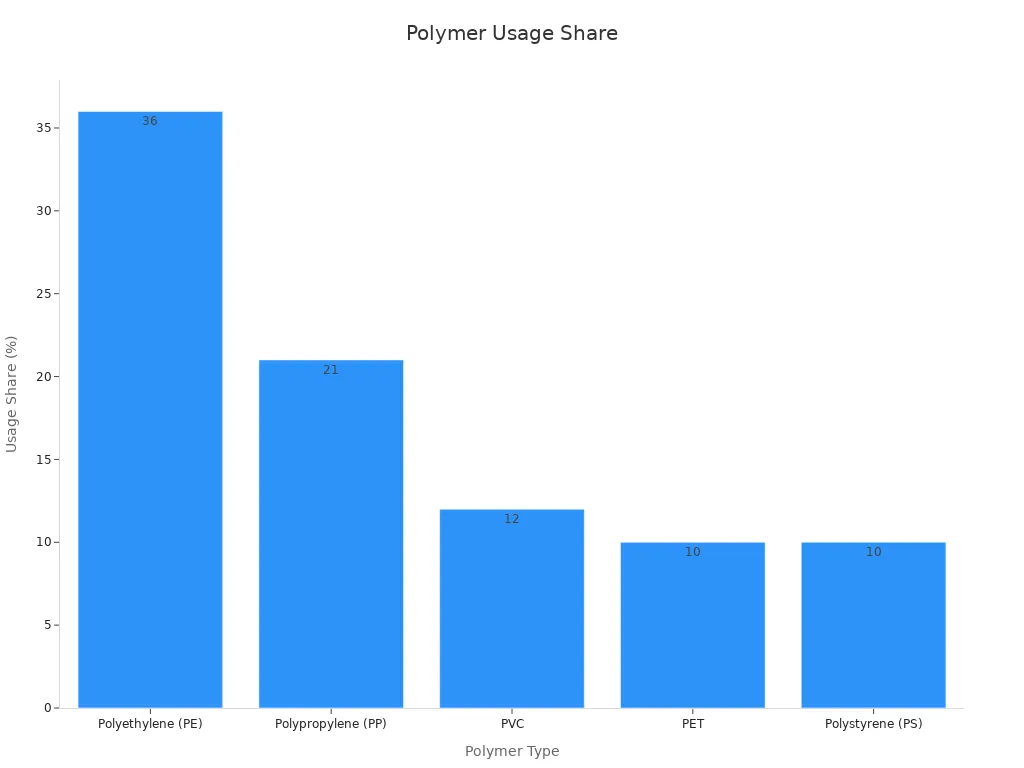
| Polymer Type | Usage Share in Packaging | Common Packaging Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 36% | Flexible packaging, pouches, bags |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 21% | Trays, lidding, bags |
| PVC | 12% | Various packaging |
| PET | 10% | Bottles, trays |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 10% | Foam packaging |
Polypropylene bags are widely used for snacks, pet food, and agricultural products.
Food-grade polypropylene bags ensure safe transport of bulk food items.
The apparel sector relies on polypropylene bags for packaging and moisture management.
Industrial packaging uses polypropylene bags for sandbags and bulk material handling.

| Feature | Polyethylene Bags | Polypropylene Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Very high, especially LDPE | Moderate, more rigid |
| Strength | Good, especially HDPE | High, supports heavier loads |
| Durability | Excellent for daily use | Superior for repeated use |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 130°C | Up to 170°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists moisture, acids, alkalis | Resists oils, solvents, chemicals |
| Clarity | Translucent to semi-transparent | High clarity, glossy finish |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Generally lower | Slightly higher |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Recyclable |
| Common Uses | Grocery, food, industrial | Food, apparel, industrial |
This table highlights the main differences between polyethylene and polypropylene bags. Polyethylene bags offer more flexibility and better performance in cold environments. Polypropylene bags provide higher heat resistance and clarity, making them suitable for packaging that requires product visibility.
Polyethylene bags: Best for flexibility, softness, and low-temperature use.
Polypropylene bags: Preferred for rigidity, clarity, and heat resistance.
Both bags: Lightweight, recyclable, and used in food, retail, and industrial packaging.
Polyethylene bags: Cost-effective and easy to produce in large quantities.
Polypropylene bags: Superior for applications needing high durability and chemical resistance.
The quick reference list uses clear headings and direct points, making it easy for users to compare key features. This structure allows readers to quickly find and understand the main differences between polyethylene and polypropylene bags.
Selecting the right bag for packaging depends on several important factors. Businesses should evaluate the appearance, flexibility, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, cost, and recyclability of each option. Polyethylene bags offer a soft, pliable feel and perform well in cold environments. These bags provide a cost-effective solution for industrial and heavy-duty packaging. Polypropylene bags stand out for their crystal-clear transparency and rigid structure. They resist heat and chemicals, making them ideal for retail, food, and medical packaging where product visibility and compliance matter.
| Feature | Polyethylene (PE) Bags | Polypropylene (PP) Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Translucent or opaque | Crystal clear |
| Flexibility | Soft, flexible | Stiff, rigid |
| Temperature Resistance | Good in cold | Good in heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Recyclability | Yes | Yes |
Tip: Consider the packaging environment, product type, and presentation needs before making a decision.
Polyethylene bags work best for industrial, heavy-duty, and protective packaging. These bags handle sharp or heavy items and shield contents from dust and light. Polypropylene bags excel in retail, food, and medical packaging. Their clarity and rigidity help display products attractively and meet strict standards. When durability is a priority, both types perform well, but polypropylene bags support heavier loads and repeated use.
Polyethylene bags: Industrial storage, shipping, and protective covers.
Polypropylene bags: Food packaging, retail displays, and medical supplies.
Sustainability plays a growing role in packaging choices. Both polyethylene and polypropylene bags are recyclable, but local facilities and collection rates affect actual recyclability. Paper bags offer biodegradability and recyclability, but they require more energy to produce and must be reused several times to offset their environmental impact. Nylon bags provide strength and reusability, but they are not biodegradable. Biodegradable bags made from materials like PLA or PHA are gaining popularity as regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly options increase. The most sustainable choice often depends on how many times a bag is reused and whether it is disposed of responsibly.
Note: Responsible reuse and proper disposal help maximize the environmental benefits of any packaging option.
Polyethylene bags deliver flexibility and cost savings, while polypropylene bags provide superior clarity and heat resistance. Selecting the right bag depends on the product’s requirements, such as strength, visibility, and temperature tolerance.
For those unsure which to choose, consider the bag’s end use: select polyethylene for softness and cold storage, or pick polypropylene for product display and heat exposure. Matching the bag type to the application ensures optimal performance and value.
Polyethylene bags offer more flexibility and softness. Polypropylene bags provide higher rigidity and clarity. Each material suits different packaging needs based on strength, appearance, and temperature resistance.
Both polyethylene and polypropylene bags meet food safety standards. Manufacturers often use them for packaging bread, produce, snacks, and frozen foods. Always check for food-grade certification before use.
Recycling facilities accept both types of bags. Collection rates and local recycling programs may vary. Clean and dry bags before recycling to improve processing efficiency.
Polyethylene bags perform well in cold environments. They resist cracking and maintain flexibility at low temperatures. Polypropylene bags may become brittle in freezing conditions.
Polypropylene bags resist oils, solvents, and many chemicals better than polyethylene bags. Polyethylene bags block moisture and oxygen more effectively. Choose based on the specific chemical exposure expected.

